Toyama: The Optimal Third Pillar of Japan’s Digital Infrastructure
Sources: Power Academy JP
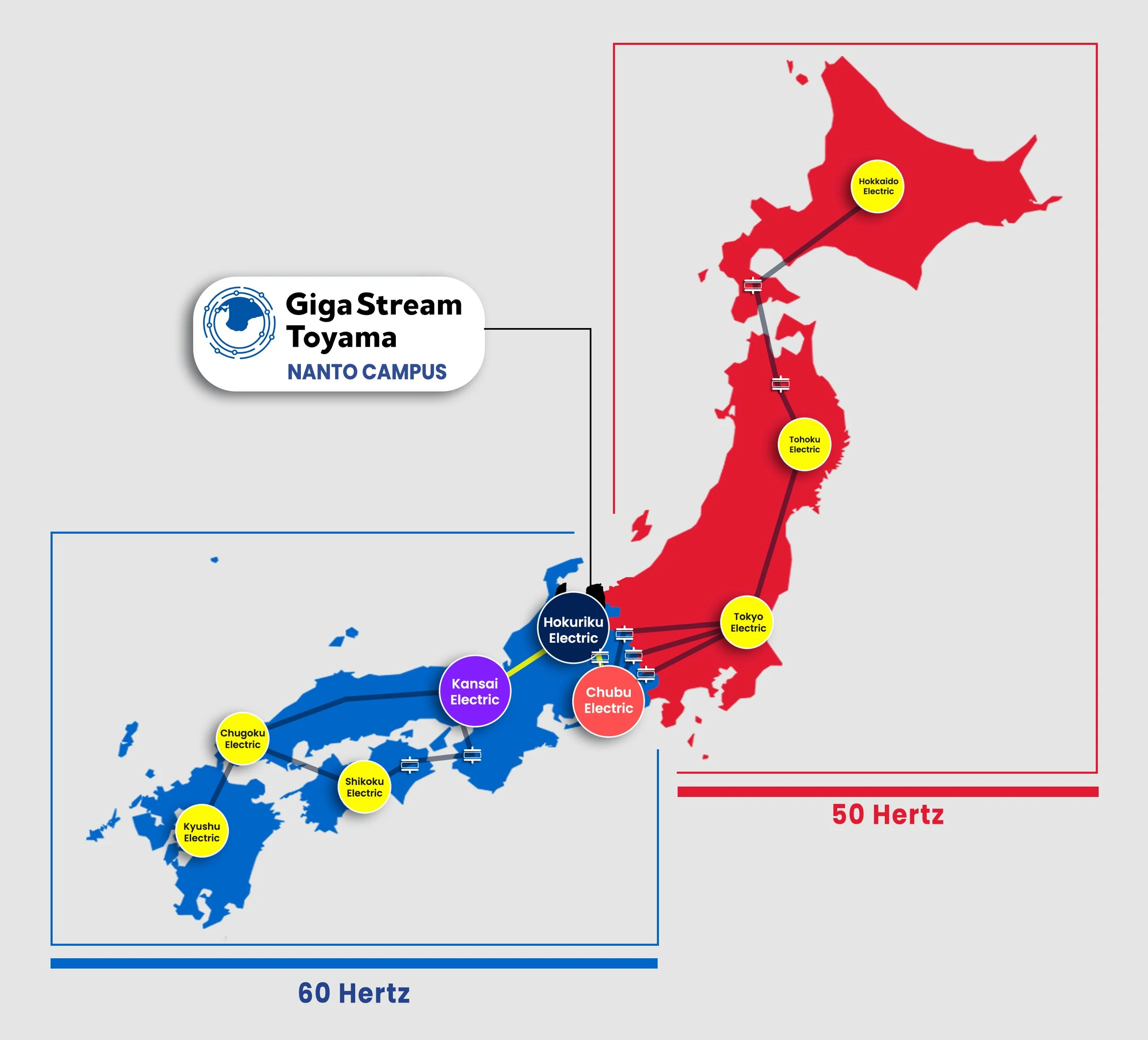
Unmatched Power Optionality & Grid Interconnection
GigaStream Toyama’s Nanto Campus is structured to deliver large-scale, fast-to-market committed power. The flagship campus features multi-grid access, supporting flexibility across future power procurement, pricing, resilience, and energy-sourcing strategies, within a region known for stable capacity and expanding renewable energy availability.
Sources: Central Disaster Management Council
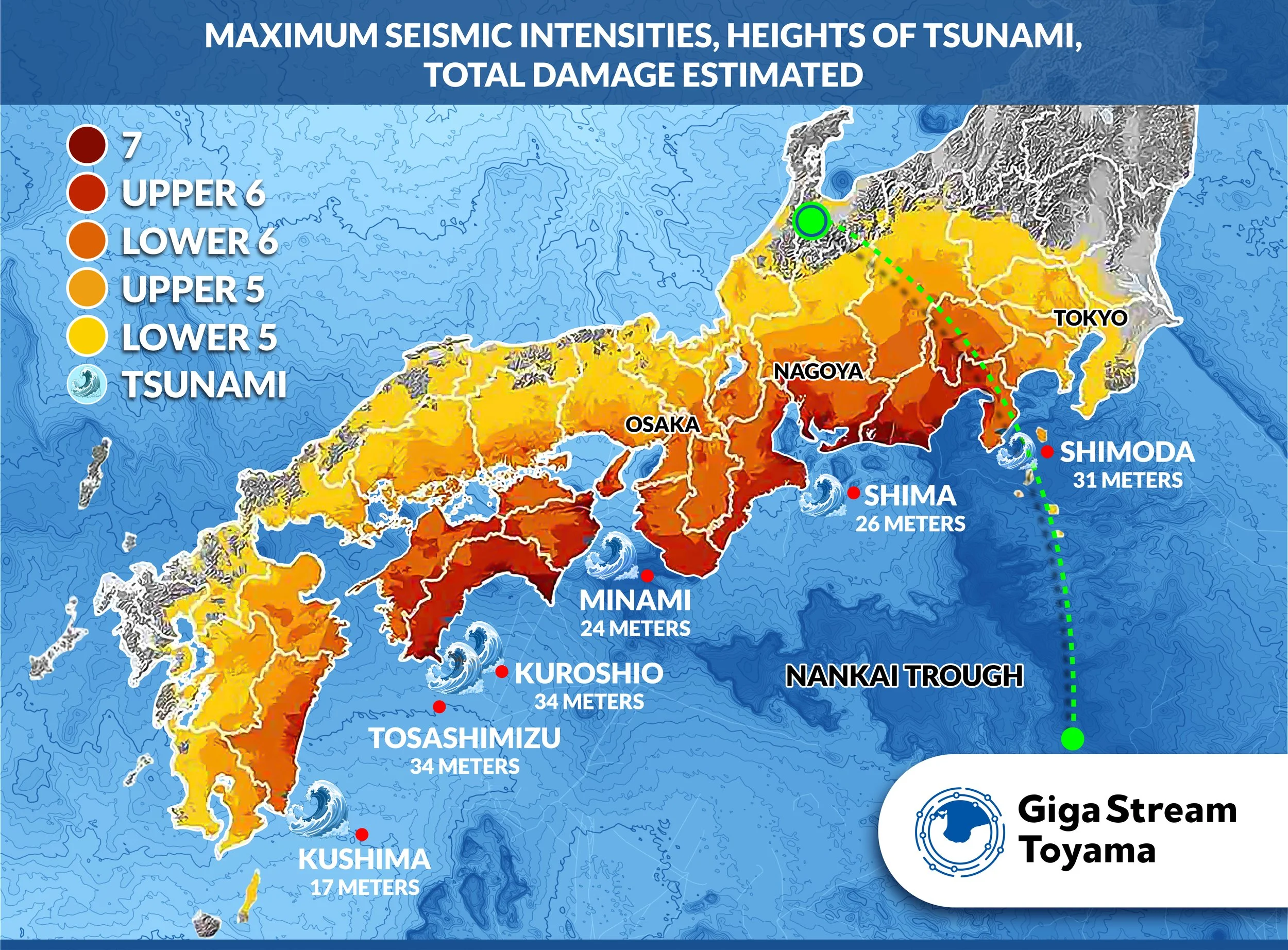
True Geographic & Seismic Redundancy
Toyama sits in an optimal location on the central western side of Japan, where seismic activity and earthquake exposure are significantly lower than in and around Tokyo and the Pacific/Nankai Trough risk zones. The region offers true geographic diversity while remaining only ~200 km from Japan’s major economic hubs—close enough for low latency, yet far enough to meaningfully diversify risk.
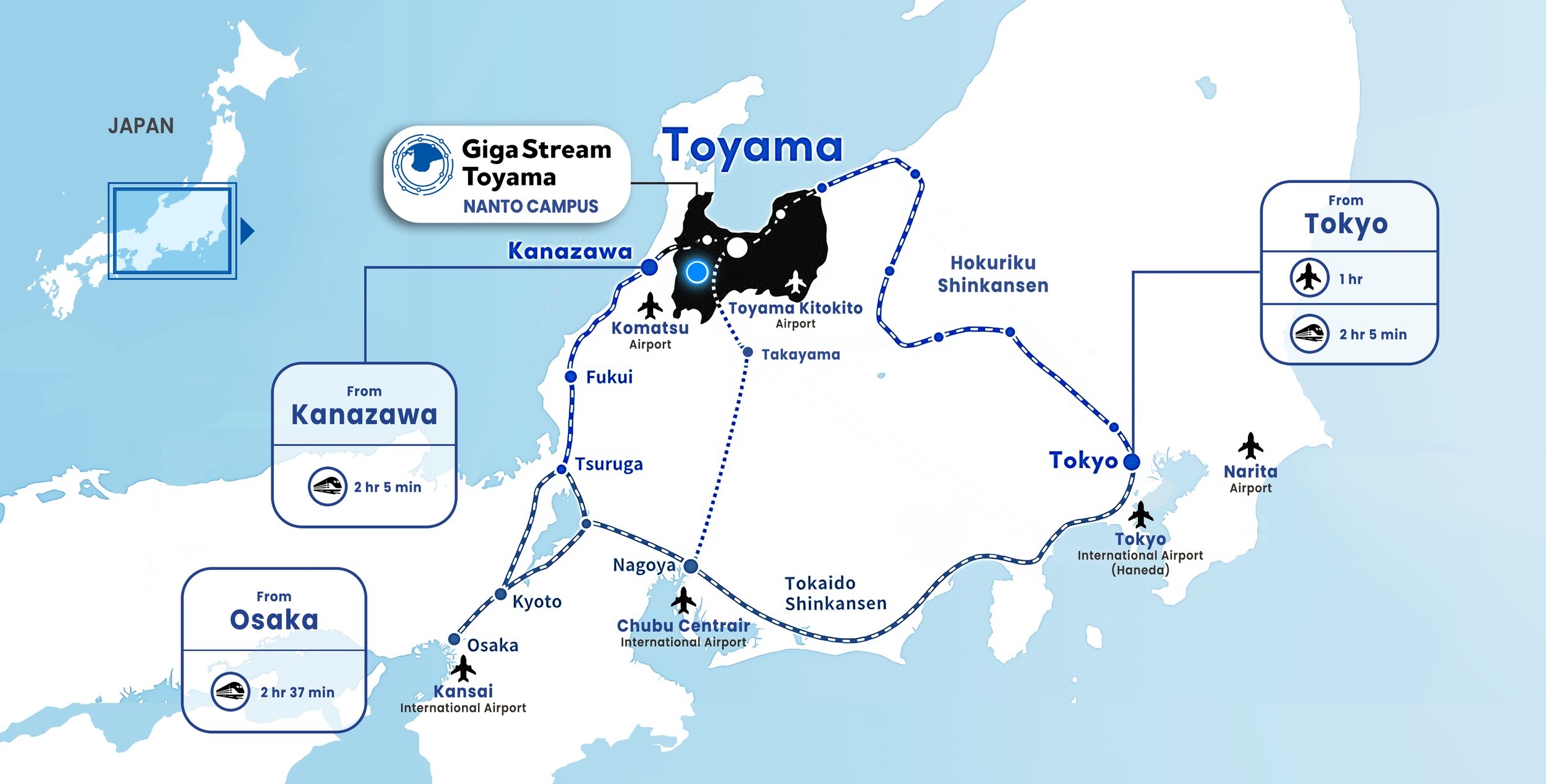
Efficient Transportation & Accessibility
Toyama offers exceptional accessibility via a combination of air and high-speed rail infrastructure. The Hokuriku Shinkansen provides direct high-speed rail access to Tokyo in approximately 2 hours and 5 minutes, while Toyama Airport and Komatsu Airport offer direct flights to major international hubs including Seoul, Shanghai, Taipei, and Hong Kong, enabling efficient regional and global connectivity.
The Nanto Campus is located in close proximity to key transport nodes—approximately 30 minutes from Kanazawa Station, 25 minutes from Shin-Takaoka Station, and 40 minutes from Toyama Station—making same-day travel from Tokyo practical for operational, commercial, and government stakeholders.
Carrier-Dense, Low-Latency Fiber Ecosystem
Located in the Hokuriku region, Toyama sits on multiple, diverse terrestrial fiber routes connecting to Tokyo, Osaka, and Nagoya—without the single points of failure common in other proposed hub locations that rely on limited crossings into the Honshu backbone. At ~200 km from Tokyo, Toyama offers latency suitable for a wide range of workloads. The region is also well positioned to connect to next-generation western Japan subsea cable systems currently under planning and government priority review.
Existing Regional Industry, Talent, and Supply Chain Strength
Toyama and the surrounding Hokuriku region have a strong industrial base with an established ecosystem of general contractors, specialty subcontractors, precision manufacturing firms, and skilled trades. This provides a scalable local workforce for construction, operations, and long-term facility support. Gigastream Toyama and partners will further enable knowledge transfer, training, and vendor ecosystem development tailored to hyperscale and AI-era data center operations.
Development Partners:
Natural Cooling Advantage and Environmental Efficiency
Toyama’s cooler year-round climate and low humidity create highly favorable conditions for efficient data center cooling, reducing energy consumption and operational overhead. These environmental advantages support sustainable designs such as liquid cooling, heat reuse systems, and renewable-integrated infrastructure. As AI and high-density compute workloads expand, Toyama’s natural climate profile provides meaningful long-term efficiency, cost stability, and environmental performance benefits.